Difference between revisions of "Template:Frieze group notations"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
↑ Frieze Patterns Mathematician John Conway created names that relate to footsteps for each of the frieze groups.
imported>Tomruen |
imported>Parcly Taxel m (no need to rely on Canadian syllabics?) |
||
| (48 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {| class=wikitable | + | {| class="wikitable sortable" |
|+ [[Frieze group]]s | |+ [[Frieze group]]s | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ![[IUC notation|IUC]] |
| − | ! | + | ![[Coxeter notation|Cox]] |
| − | ! | + | ![[Schoenflies_notation|Schön]]<sup>*</sup><BR>[[Group (mathematics)|Struct.]] |
| + | !Diagram<sup>§</sup><BR>[[Orbifold notation|Orbifold]] | ||
| + | !Examples<BR>and [[John Horton Conway|Conway]] nickname<ref>[https://www.maa.org/sites/default/files/images/upload_library/4/vol1/architecture/Math/seven.html Frieze Patterns] Mathematician John Conway created names that relate to footsteps for each of the frieze groups.</ref> | ||
| + | !Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ![[ | + | !p1||[∞]<sup>+</sup><BR>{{CDD|node_h2|infin|node_h2}}||C<sub>∞</sub><BR>[[Infinite cyclic group|Z<sub>∞</sub>]] |
| − | + | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Frieze group 11.png|100px]]<BR>∞∞|| style="text-align:center;" |'''<big>F F F F F F F F</big>'''<BR>[[File:Frieze example p1.png|150px]]<BR>[[File:Frieze hop.png|150px]]<BR>hop | |
| − | + | ||(T) Translations only:<BR>This group is singly generated, by a translation by the smallest distance over which the pattern is periodic. | |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !p11g||[∞<sup>+</sup>,2<sup>+</sup>]<BR>{{CDD|node_h2|infin|node_h4|2x|node_h2}}||S<sub>∞</sub><BR>Z<sub>∞</sub> |
| − | || | + | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Frieze group 1g.png|100px]]<BR>∞×|| style="text-align:center;" |'''<big>Γ L Γ L Γ L Γ L</big>'''<BR>[[File:Frieze example p11g.png|150px]]<BR>[[File:Frieze step.png|150px]]<BR>step |
| − | + | |(TG) Glide-reflections and Translations:<BR>This group is singly generated, by a glide reflection, with translations being obtained by combining two glide reflections. | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !p1m1||[∞]<BR>{{CDD|node|infin|node}}||C<sub>∞v</sub><BR>[[infinite dihedral group|Dih<sub>∞</sub>]] |
| − | ||( | + | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Frieze group m1.png|100px]]<BR>*∞∞|| style="text-align:center;" |'''<big>Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ</big>'''<BR>[[File:Frieze example p1m1.png|150px]]<BR>[[File:Frieze sidle.png|150px]]<BR>sidle |
| + | ||(TV) Vertical reflection lines and Translations:<BR>The group is the same as the non-trivial group in the one-dimensional case; it is generated by a translation and a reflection in the vertical axis. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !p2||[∞,2]<sup>+</sup><BR>{{CDD|node_h2|infin|node_h2|2x|node_h2}}||D<sub>∞</sub><BR>Dih<sub>∞</sub> |
| − | ||( | + | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Frieze group 12.png|100px]]<BR>22∞|| style="text-align:center;" |'''<big>S S S S S S S S</big>'''<BR>[[File:Frieze example p2.png|150px]]<BR>[[File:Frieze spinning hop.png|150px]]<BR>spinning hop |
| + | |(TR) Translations and 180° Rotations:<BR>The group is generated by a translation and a 180° rotation. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !p2mg||[∞,2<sup>+</sup>]<BR>{{CDD|node|infin|node_h2|2x|node_h2}}||D<sub>∞d</sub><BR>Dih<sub>∞</sub> |
| − | ||( | + | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Frieze group mg.png|100px]]<BR>2*∞|| style="text-align:center;" |'''<big>V Λ V Λ V Λ V Λ</big>'''<BR>[[File:Frieze example p2mg.png|150px]]<BR>[[File:Frieze spinning sidle.png|150px]]<BR>spinning sidle |
| + | |(TRVG) Vertical reflection lines, Glide reflections, Translations and 180° Rotations:<BR>The translations here arise from the glide reflections, so this group is generated by a glide reflection and either a rotation or a vertical reflection. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !p11m||[∞<sup>+</sup>,2]<BR>{{CDD|node_h2|infin|node_h2|2|node}}||C<sub>∞h</sub><BR>Z<sub>∞</sub>×Dih<sub>1</sub> |
| − | ||( | + | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Frieze group 1m.png|100px]]<BR>∞*|| style="text-align:center;" |'''<big>B B B B B B B B</big>'''<BR>[[File:Frieze example p11m.png|150px]]<BR>[[File:Frieze jump.png|150px]]<BR>jump |
| + | |(THG) Translations, Horizontal reflections, Glide reflections:<BR>This group is generated by a translation and the reflection in the horizontal axis. The glide reflection here arises as the composition of translation and horizontal reflection | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | !p2mm||[∞,2]<BR>{{CDD|node|infin|node|2|node}}||D<sub>∞h</sub><BR>Dih<sub>∞</sub>×Dih<sub>1</sub> |
| − | || | + | | style="text-align:center;" |[[File:Frieze group mm.png|100px]]<BR>*22∞|| style="text-align:center;" |<big>'''H H H H H H H H'''</big><BR>[[File:Frieze example p2mm.png|150px]]<BR>[[File:Frieze spinning jump.png|150px]]<BR>spinning jump |
| − | + | |(TRHVG) Horizontal and Vertical reflection lines, Translations and 180° Rotations:<BR>This group requires three generators, with one generating set consisting of a translation, the reflection in the horizontal axis and a reflection across a vertical axis. | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | || | ||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
:<sup>*</sup>Schönflies's point group notation is extended here as infinite cases of the equivalent dihedral points symmetries | :<sup>*</sup>Schönflies's point group notation is extended here as infinite cases of the equivalent dihedral points symmetries | ||
| − | + | :<sup>§</sup>The diagram shows one [[fundamental domain]] in yellow, with reflection lines in blue, glide reflection lines in dashed green, translation normals in red, and 2-fold gyration points as small green squares. | |
Latest revision as of 11:23, 26 October 2020
| IUC | Cox | Schön* Struct. |
Diagram§ Orbifold |
Examples and Conway nickname[1] |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | [∞]+ |
C∞ Z∞ |
 ∞∞ |
F F F F F F F F hop |
(T) Translations only: This group is singly generated, by a translation by the smallest distance over which the pattern is periodic. |
| p11g | [∞+,2+] |
S∞ Z∞ |
 ∞× |
Γ L Γ L Γ L Γ L step |
(TG) Glide-reflections and Translations: This group is singly generated, by a glide reflection, with translations being obtained by combining two glide reflections. |
| p1m1 | [∞] |
C∞v Dih∞ |
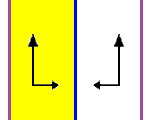 *∞∞ |
Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ Λ sidle |
(TV) Vertical reflection lines and Translations: The group is the same as the non-trivial group in the one-dimensional case; it is generated by a translation and a reflection in the vertical axis. |
| p2 | [∞,2]+ |
D∞ Dih∞ |
 22∞ |
S S S S S S S S spinning hop |
(TR) Translations and 180° Rotations: The group is generated by a translation and a 180° rotation. |
| p2mg | [∞,2+] |
D∞d Dih∞ |
 2*∞ |
V Λ V Λ V Λ V Λ spinning sidle |
(TRVG) Vertical reflection lines, Glide reflections, Translations and 180° Rotations: The translations here arise from the glide reflections, so this group is generated by a glide reflection and either a rotation or a vertical reflection. |
| p11m | [∞+,2] |
C∞h Z∞×Dih1 |
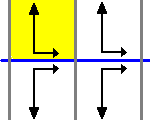 ∞* |
B B B B B B B B jump |
(THG) Translations, Horizontal reflections, Glide reflections: This group is generated by a translation and the reflection in the horizontal axis. The glide reflection here arises as the composition of translation and horizontal reflection |
| p2mm | [∞,2] |
D∞h Dih∞×Dih1 |
 *22∞ |
H H H H H H H H spinning jump |
(TRHVG) Horizontal and Vertical reflection lines, Translations and 180° Rotations: This group requires three generators, with one generating set consisting of a translation, the reflection in the horizontal axis and a reflection across a vertical axis. |
- *Schönflies's point group notation is extended here as infinite cases of the equivalent dihedral points symmetries
- §The diagram shows one fundamental domain in yellow, with reflection lines in blue, glide reflection lines in dashed green, translation normals in red, and 2-fold gyration points as small green squares.