Difference between revisions of "Template:Comparison satellite navigation orbits"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>Cmglee (Fix caption to match updated SVG) |
imported>Cmglee (Explain orbital period calculation) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
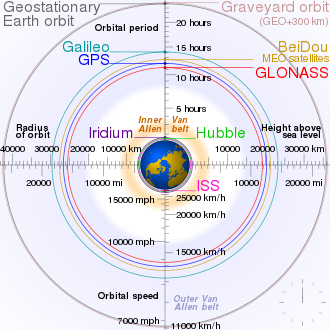
| − | [[Image:Comparison_satellite_navigation_orbits.svg|thumb|Comparison of [[GPS]], [[GLONASS]], [[Galileo_(satellite_navigation)|Galileo]] and [[Compass_navigation_system|Compass (medium earth orbit satellites)]] [[satellite navigation system]] orbits with the [[International Space Station]] orbit, the [[Hubble Space Telescope]] orbit, [[Geostationary Earth Orbit]] and the nominal size of the [[Earth]]. The [[Moon]]'s orbit is 9.1 times larger (in radius and length) than geostationary orbit.]] | + | [[Image:Comparison_satellite_navigation_orbits.svg|thumb|Comparison of [[GPS]], [[GLONASS]], [[Galileo_(satellite_navigation)|Galileo]] and [[Compass_navigation_system|Compass (medium earth orbit satellites)]] [[satellite navigation system]] orbits with the [[International Space Station]] orbit, the [[Hubble Space Telescope]] orbit, [[Geostationary Earth Orbit]] and the nominal size of the [[Earth]]. The [[Moon]]'s orbit is 9.1 times larger (in radius and length) than geostationary orbit.<ref>Orbital periods are calculated using the relation 4π²''R''³=''T''²''GM'', where ''R'' = radius of orbit in metres, ''T'' = orbital period in seconds, ''G'' = gravitational constant ≈ 6.673{{e|-11}} Nm²/kg², ''M'' = mass of Earth ≈ 5.98{{e|24}} kg.</ref>]] |
Revision as of 13:28, 7 October 2011

Comparison of GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and Compass (medium earth orbit satellites) satellite navigation system orbits with the International Space Station orbit, the Hubble Space Telescope orbit, Geostationary Earth Orbit and the nominal size of the Earth. The Moon's orbit is 9.1 times larger (in radius and length) than geostationary orbit.[1]
- ↑ Orbital periods are calculated using the relation 4π²R³=T²GM, where R = radius of orbit in metres, T = orbital period in seconds, G = gravitational constant ≈ 6.673×10−11 Nm²/kg², M = mass of Earth ≈ 5.98×1024 kg.